In today’s fast-paced digital world, cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure and deliver services. It has introduced various service models, including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), each offering distinct advantages and use cases. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into these cloud service models to help you understand their differences and make informed decisions for your business.
Cloud Computing Overview
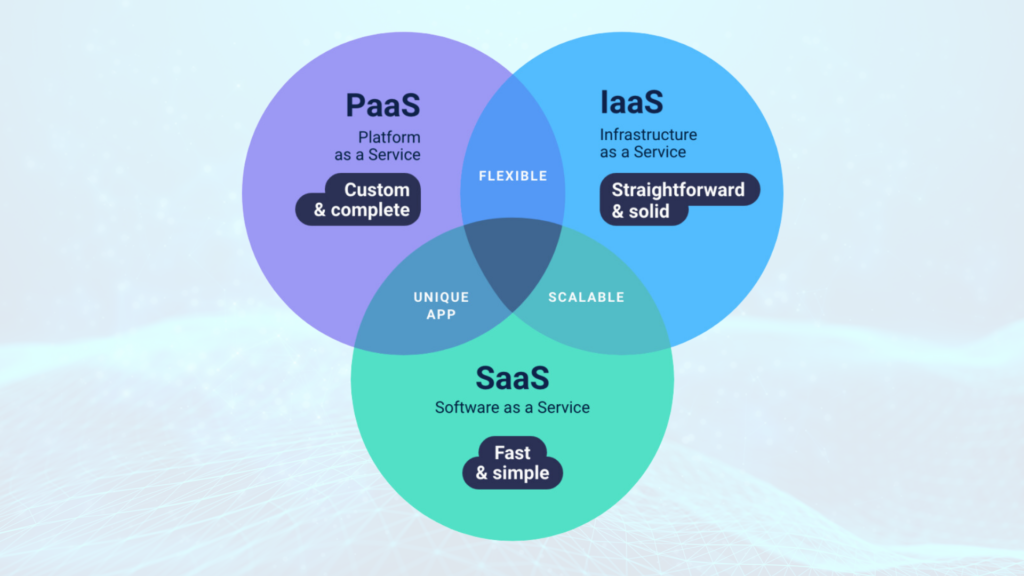
Before we dive into the specifics of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, let’s start with a brief overview of cloud computing.
Cloud computing (Cloud Service Models)
is a technology that enables users to access and utilize a wide range of computing resources (such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics) over the internet. This eliminates the need for organizations to invest in and manage physical hardware, reducing costs and increasing agility.
Now, let’s explore the three primary cloud service models.
SaaS (Cloud Service Models)

SaaS, or Software as a Service, is one of the most common and user-friendly cloud service models. It delivers software applications directly to end-users over the internet on a subscription basis. In a SaaS model, the software is hosted, maintained, and updated by a third-party provider, allowing users to access it via a web browser.
Key Characteristics of SaaS:

Accessibility (Cloud Service Models)
SaaS applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection and a compatible device, making them highly convenient for users.
Cloud Service Models & Automatic Updates
SaaS providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
Scalability of Cloud Service Models
SaaS solutions can easily scale up or down to accommodate changing user needs or business growth, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes.
SaaS Use Cases:
- Office Productivity: Examples include Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Zoom for online meetings.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Salesforce and HubSpot offer SaaS CRM solutions.
- Project Management: Tools like Trello and Asana are popular for team collaboration and project management.
- Collaboration: Slack and Microsoft Teams facilitate real-time communication and document sharing.
Advantages of SaaS:
- Cost-Effective: SaaS eliminates the need for organizations to invest in hardware and software infrastructure, reducing upfront costs.
- Rapid Deployment: Users can start using SaaS applications immediately after subscription, accelerating time-to-market.
- Low Maintenance: Providers handle updates, security, and maintenance, reducing the burden on IT teams.
- Accessibility: Users can work from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting remote work flexibility.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)

PaaS, or Platform as a Service, is a cloud service model designed to provide developers with a platform and environment to build, deploy, and manage applications. It abstracts the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on coding and application development.
Key Characteristics of PaaS:
- Development Tools: PaaS platforms offer a wide range of development tools, including databases, application frameworks, and middleware, simplifying the development process.
- Automated Deployment: Developers can easily deploy and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure, streamlining the development lifecycle.
- Scalability: PaaS solutions offer scalability, allowing applications to handle varying workloads, making them ideal for dynamic and growing businesses.
PaaS Use Cases:
- Web Application Development: PaaS is well-suited for developing web applications, APIs, and microservices, providing the necessary tools and resources.
- DevOps: It facilitates continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, enabling faster and more efficient development processes.
- Database Management: PaaS platforms provide managed database services, simplifying data storage and retrieval.
Advantages of PaaS:
- Streamlined Development: Developers can focus on coding and innovation, as the underlying infrastructure is managed by the PaaS provider.
- Scalability: Applications can scale seamlessly to accommodate user demand, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- Cost-Efficiency: PaaS eliminates the need to manage and maintain infrastructure, reducing operational costs.
- Collaboration: PaaS encourages collaboration among development teams, fostering innovation.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)

IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service, represents the fundamental layer of cloud computing. It provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing users to rent virtual hardware, including virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking components.
Key Characteristics of IaaS:
- Flexibility: Users have the flexibility to configure and manage virtualized resources according to their specific requirements, offering full control over the infrastructure.
- Virtualization: IaaS relies heavily on virtualization technologies to abstract and manage physical hardware, optimizing resource utilization.
- Full Control: IaaS users have complete control over the operating system, applications, and configurations, making it suitable for complex and customized setups.
IaaS Use Cases:
- Hosting Websites: IaaS is commonly used to host websites and web applications, providing the necessary infrastructure and scalability.
- Development and Testing: Developers can create and test applications in isolated environments, reducing development costs.
- Data Backup and Storage: IaaS offers scalable storage solutions for data backup, archiving, and disaster recovery.
Advantages of IaaS:
- Scalability: Users can scale resources up or down as needed, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Customization: IaaS provides full control over infrastructure configurations, making it suitable for businesses with unique requirements.
- Cost Savings: By eliminating the need to invest in and maintain physical hardware, IaaS can lead to significant cost savings.
- Disaster Recovery: IaaS can be used for backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring data availability and business continuity.
Comparing SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
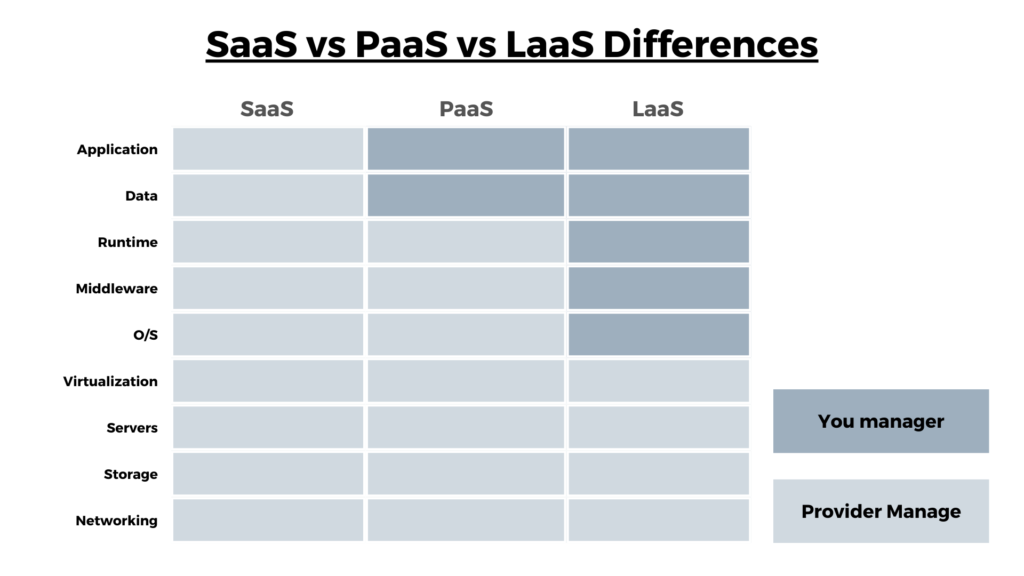
Now that we have a clear understanding of each cloud service model, let’s compare them based on key criteria to help you choose the most suitable option for your business needs.
1. User Focus:
- SaaS: Targeted at end-users who rely on software applications for their day-to-day tasks and operations.
- PaaS: Primarily focused on developers and IT teams engaged in application development, deployment, and management.
- IaaS: Geared toward IT administrators responsible for managing the underlying infrastructure and configuring virtual resources.
2. Management Responsibility:
- SaaS: Providers handle software maintenance, updates, and security, reducing the management burden on end-users.
- PaaS: Developers manage applications and their code, while the PaaS provider takes care of the underlying platform, including the runtime environment and infrastructure.
- IaaS: Users have complete control over the operating system, applications, and configurations, requiring them to manage and maintain the virtual infrastructure.
3. Cloud Service Models & Scalability:
- SaaS: Scalability is limited to what the SaaS provider offers. Users can typically scale the number of licenses or seats but have limited control over underlying infrastructure scalability.
- PaaS: Offers more scalability options for applications, making it suitable for businesses experiencing variable workloads.
- IaaS: Provides the greatest flexibility in terms of scaling resources up or down based on demand, making it ideal for businesses with unpredictable resource requirements.
4. Control:
- SaaS: Users have limited control, as SaaS is primarily designed to provide ready-to-use software solutions. Customizations are often limited.
- PaaS: Developers have control over application code and configurations but do not manage the underlying infrastructure.
- IaaS: Offers the most control, allowing users to configure and manage the operating system, applications, and infrastructure components.
5. Cost Structure:
- SaaS: Typically, subscription-based pricing with monthly or annual fees. Users pay for the number of licenses or seats.
- PaaS: Pricing varies and is often based on usage, with additional charges for specific services or features.
- IaaS: Typically follows a pay-as-you-go model, with costs based on resource usage, such as virtual machine hours, storage capacity, and data transfer.
6. Cloud Service Models & Use Cases:
- SaaS: Ideal for businesses that need ready-to-use software applications without the complexity of managing infrastructure. Commonly used for office productivity, CRM, project management, and collaboration.
- PaaS: Well-suited for developers building and deploying web applications, APIs, microservices, and applications requiring a streamlined development process.
- IaaS: Best for businesses requiring complete control over infrastructure configurations, hosting websites and web applications, and managing complex IT environments.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Model
Selecting the appropriate cloud service model depends on your specific business needs, objectives, and constraints. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
1. Choose SaaS if:
- You need access to software applications with minimal setup and maintenance.
- Rapid deployment and scalability are critical for your business.
- Cost-effective software solutions without infrastructure management are preferred.
- Your business relies on collaboration tools, office productivity suites, or customer relationship management software.
2. Choose PaaS if:
- You are a developer or part of an IT team focused on application development.
- Streamlined development processes, continuous integration, and deployment are essential.
- You require a platform with development tools, databases, and middleware.
- Scalability and flexibility in managing applications are key requirements.
3. Choose IaaS if:
- You need complete control over infrastructure configurations and customization.
- Your business requires hosting websites, web applications, or complex IT environments.
- You have unpredictable resource requirements and need to scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Data backup, disaster recovery, or testing and development environments are essential.
Conclusion in Cloud Service Models

Understanding the differences between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS is crucial for making informed decisions about cloud service adoption in your organization. Each model offers unique benefits and caters to specific business requirements. Whether you prioritize ease of use, streamlined development, or full infrastructure control, the cloud service model you choose can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, agility, and cost-effectiveness.
To make the right choice, assess your current needs and future growth plans, consider your IT expertise, and evaluate the importance of factors like cost savings, scalability, and management control. By aligning your cloud service model with your business goals, you can harness the power of cloud computing to drive innovation and success.
Remember that the cloud landscape is continuously evolving, so it’s essential to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies to leverage the full potential of cloud services for your organization.
Whether you opt for SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS—or a combination of these models—cloud computing has undoubtedly revolutionized the way businesses operate, enabling them to adapt, innovate, and thrive in a rapidly changing digital world.
As you embark on your cloud journey, keep in mind that your choice of cloud service model is just the beginning. To fully harness the benefits of cloud computing, consider partnering with experienced cloud providers and experts who can guide you through implementation, optimization, and ongoing management.
Investing in the right cloud solutions today can position your organization for success tomorrow, providing a solid foundation for growth, agility, and competitive advantage in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Pantheon Digital
www.pantheondigitals.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS?
SaaS delivers ready-to-use software, PaaS provides a platform for application development, and IaaS offers virtualized infrastructure.
How do I determine which cloud service model is right for my business?
Assess your specific needs, such as control, scalability, and development requirements, to align with the most suitable cloud service model.
Are there any security concerns with SaaS, PaaS, or IaaS?
Security varies but can be managed with best practices. Consider factors like data encryption, access controls, and compliance when choosing a model.
What are some popular examples of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS providers?
Examples include Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace (SaaS), AWS Elastic Beanstalk (PaaS), and Amazon EC2 (IaaS).
Can I combine different cloud service models within my organization?
Yes, many organizations use a mix of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS to meet various needs. It’s called a hybrid cloud approach and offers flexibility.


OSm
Thanks